SQL Revision Part -1
Let’s start with
SQL basics.
SQL is a standard
language for storing, manipulating and retrieving data in databases.
We will revise all the command and syntax used in the SQL. I assume that reader is well acquainted with the SQL or even has some idea about it. I hope you have worked with “imdb” dataset and know how to load it in the MySQL command line client. We will extensively use imdb database in the entire bootcamp
1. USE :
The "USE imdb " command will load the
database imdb into SQL command line.
Displays all the tables present in the
database.
It describes the structure of the Table.
Used to select data from a database.
Syntax:
SELECT column1, column2,
...
FROM table_name;
If
you have to select every column along with its data from movies table :
SELECT * FROM movies;
If you have to select every column along with its data from
directors table :
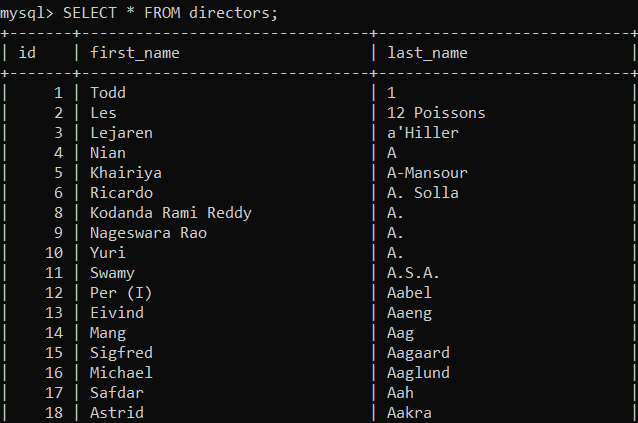
SELECT * FROM directors;
To
select only a particular column from a table use the following command:
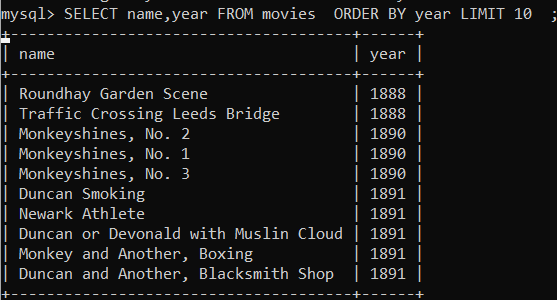
SELECT name, year FROM
movies;
5. LIMIT:
Used to
specify the number of records to return. As the database contains a large
number of records, to load all of it impacts performance, therefore LIMIT is
used.
Syntax:
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
LIMIT number;
Example:
6. OFFSET
Used to identify the starting point to return rows from result.
Syntax :
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
OFFSET rows_to_skip ;
Example:
Without Offset
With Offset:
7. ORDER BY
Used to sort the result-set in ascending or descending order. It sorts the records in ascending order by default. To sort the records in descending order, use the DESC keyword.
Syntax
SELECT column1, column2,
...
FROM table_name
ORDER BY column1,
column2, ... ASC|DESC;
Example:
Ascending
SELECT name,rankscore,year FROM
movies ORDER BY year DESC LIMIT 10;DESCENDEING
8. DISTINCT:
Used to return only distinct values
Syntax :
SELECT DISTINCT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name;
Example:
Without DISTINCT
9. WHERE
Used to filter records
Syntax :
SELECT column1, column2,
...
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
Example:
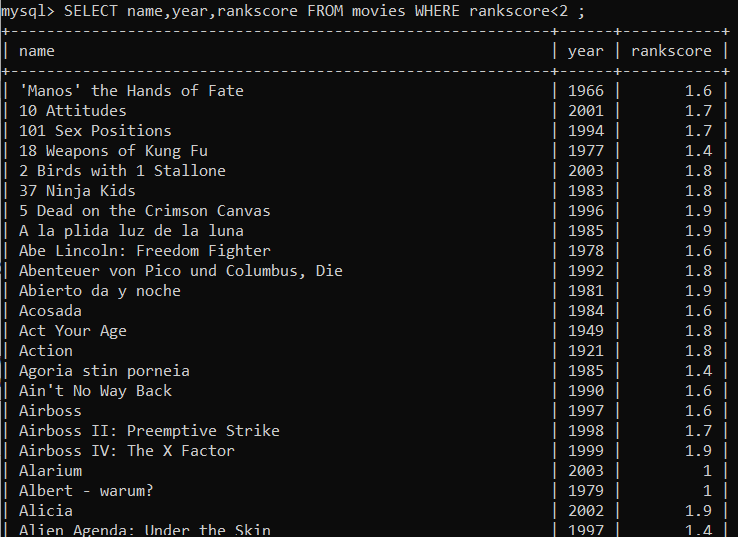
SELECT
name,year,rankscore FROM movies WHERE rankscore>9.1 ;















Comments
Post a Comment